14 - Sample size for fixed pool size and uncertain test sensitivity and specificity
This program calculates the approximate numbers of pools required for a range of pool sizes and specified values for estimated prevalence and desired confidence and precision of the estimate, assuming fixed pool sizes and a test with unknown (uncertain) sensitivity and specificity. Uncertainty associated with the point estimates of test sensitivity and specificity is incorporated through the inclusion of additional variance associated with the sample size used to determine the values used for these parameters. The smaller the sample size, the greater the uncertainty about the true values for sensitivity and/or specificity and hence the greater the uncertainty about the resulting prevalence estimate, resulting in an increased overall sample size to provide the same level of confidence in the estimate. These calculations are based on a re-arrangement of the formulae use to estimate asymptotic confidence limits for pooled prevalence estimates with unknown test sensitivity and specificity (Method 4).
The required number of pools (m) to estimate the true prevalence with the desired precision is
calculated as: 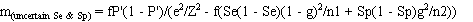
where:
- p = assumed true prevalence;
- k = pool size;
- Se = test sensitivity;
- Sp = test specificity;
- n1 = the sample size for estimating the sensitivity of the test;
- n2 = the sample size for estimating the specificity of the test;
- e = the acceptable error (desired precision); and
- Z = the standardised normal variate corresponding to the desired level of confidence.
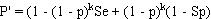
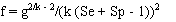
and:
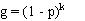
Prevalence estimates calculated from pooled testing may be upwardly biased, particularly as the probability of all pools testing positive increases (high prevalence and/or small numbers of large pools). Therefore, it is advisable to select a lower value for pool size and test a larger number of smaller pools to minimise potential bias in the result, particularly if prevalence is likely to be high. Unlike the situation with a perfect test, it is not possible to determine an optimum pool size to minimise the variance of the estimate if test sensitivity and specificity are uncertain.
Required inputs for this analysis are:
- the assumed true prevalence;
- assumed test sensitivity;
- assumed test specificity;
- sample size for estimating the sensitivity of the test;
- sample size for estimating the specificity of the test;
- the desired level of precision (or acceptable error); and
- the desired level of confidence in the result.
For example, you might wish to estimate the prevalence where the true value is assumed to be about 0.01 (1%), and you wish to have 95% (0.95) confidence that the true value is within +/- 0.005 (0.5%) of your estimate, with a test that has a sensitivity of 0.9 (90%) and specificity of 0.99 (99%) and where sensitivity and specificity were estimated using sample sizes of 100 and 1000 respectively. The assumed prevalence, desired precision and level of confidence must all be >0 and <1. Test sensitivity and specificity must both be >0 and <=1. Sample sizes for estimating sensitivity and specificity must be positive integers. The larger the sample size the lower the uncertainty and hence the greater the confidence achieved in the estimate.
You can also input a suggested pool size if desired, and the program will calculate the corresponding number of pools to be tested for that pool size (in addition to predetermined pool sizes). Suggested pool size is ignored if it is zero.
Output from the analysis is:
- the number of pools required for the input-scenario and the suggested pool size;
- a table of the numbers of pools (and total number of samples) required for the input-scenario for various pool sizes ranging from 1 to 500; and
- a graph of number of pools vs pool size.
« Previous Next »





